氢催化剂分析
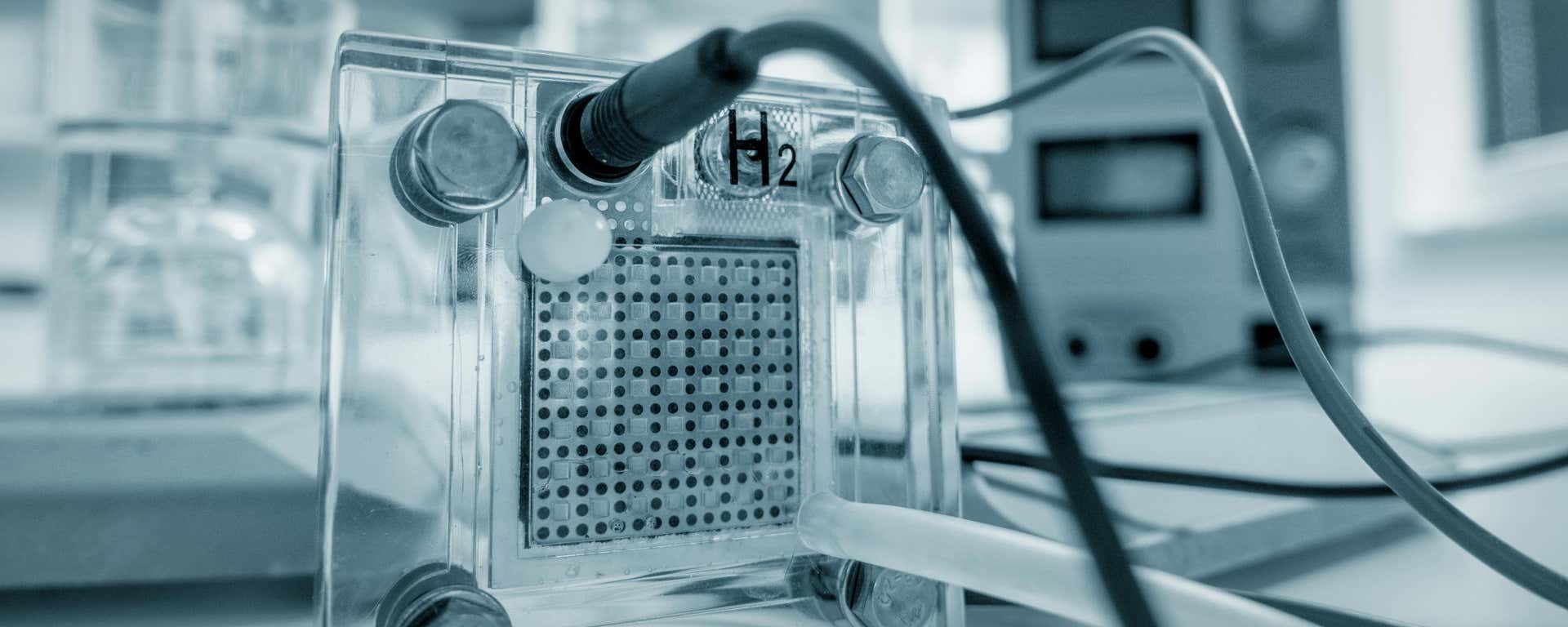

氢气作为一种清洁能源载体,可以减少各个行业对化石燃料的依赖,从而显著帮助实现脱碳目标:
氢气为 60% 以上的高温室气体排放应用提供支持,并且预计到 2050 年,氢气将贡献全球碳减排量的 20% 以上,因此它对于实现净零排放的未来至关重要。
氢催化剂对于提高氢气的生产、储存和利用效率至关重要。它们能够在多个技术领域中发挥作用:
氢经济的关键组成部分包括:
技术:
材料:吸附剂、膜、催化剂
测量目标:
技术
氢气可以储存为:
材料:吸附剂、催化剂
测量目标:
技术
氢气用途广泛:
材料:膜、催化剂、吸附剂
测量目标:

体积小巧、功能强大的便携式 XRF 分析仪

高性能气体吸附
