Gene therapy is the process by which genetic material is delivered, by means of a vector, to patients for a therapeutic purpose. Vectors are delivery vehicles - usually a virus or a liposome - used to transport the genetic material to target cells in the body.
Both cationic and anionic liposomes are currently being investigated as vectors for gene therapy and their effectiveness in transfection is being studied by research groups and pharmaceutical companies.
Cationic liposomes (positively charged) are complexed with DNA (plasmids) Fig. 1. The liposome:DNA ratio is seen to be essential for optimal transfection.
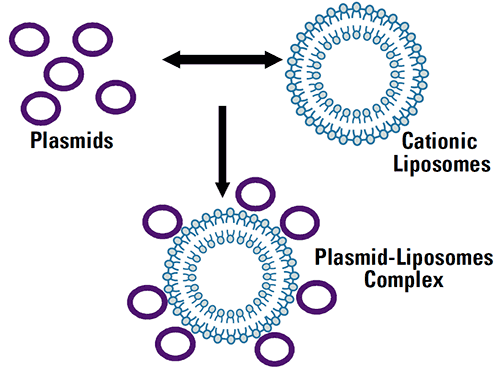
|
Zeta potential measurements can be used to optimise the ratio required for particular liposomes with various plasmids Fig 2. The plot also shows the z-average diameters of the complex formed at various plasmid:liposome ratios obtained from photon correlation spectroscopy (PCS) measurements. When the complex has either a high negative or positive zeta potential, the size is around 90nm.
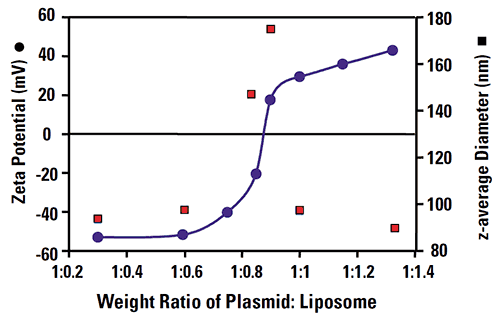
|
However, when the zeta potential approaches the iso-electric point, the z-average diameter increases indicating aggregation of the complex. Zeta potential measurements in conjunction with PCS sizing measurements allows for detailed characterisation of such plasmid: liposome complexes.
Anionic liposomes are used to encapsulate DNA. Negatively charged DNA needs to be condensed into small particles by adding some kind of compacting agent such as positively charged polylysine before encapsulation. (Fig. 3)
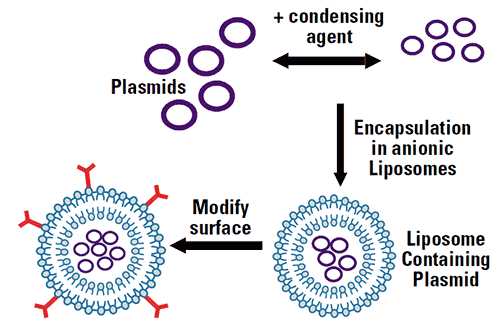
|
Zeta potential measurements can be used to determine the amount of compacting agent required to reach neutrality for high encapsulation efficiency (Fig. 4). In addition, any subsequent modification to the surface of the liposome can be investigated by monitoring the change in the measured zeta potential.
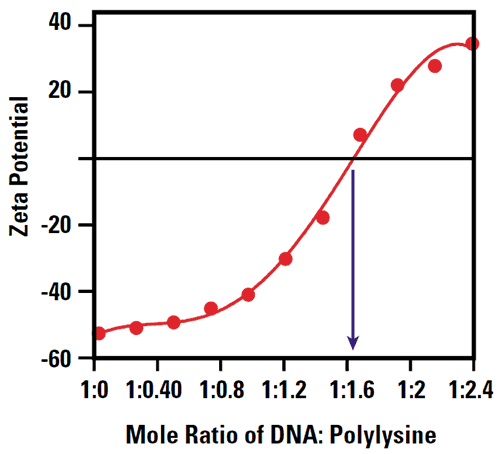
|
Lipofectin® (Liposomal transfection agent) is a commercially available liposome preparation for transfection. The cationic liposomes consisting of DOPE and DOTMA DNA are complexed with the Lipofectin. Research is on-going into the developing complexes of Lipofectin, DNA and receptor- specific peptides. Zeta potential measurements are used to determine the charge of the resulting complex.
Much work is being done in the development of vectors to incorporate specific molecules. Liposomal systems containing certain cell surface receptor- specific peptides are being developed. The use of antibodies, either covalently attached onto the surface of neutral and anionic liposomes or used in a complex, is also being investigated. Zeta potential measurements are being used to develop the most efficient formulations of liposomes:peptides:DNA complexes for transfection studies in vivo and in vitro.