在该应用指南中,我们将会介绍在进行纳米毒理学及生态毒理学研究之前,NanoSight系列仪器如何利用纳米颗粒跟踪分析(NTA)技术来确定纳米颗粒在试验介质中的状态,尤其是其粒度、粒度分布和浓度。
工程纳米颗粒(NP)的开发和使用发展迅速,相比之下其可能造成的风险进行评估与管理的方法始终相对滞后。 纳米级粒度所带来的新特性是对纳米材料的性能作出担保的重要依据。 即使散装产品的毒理学特征已得到充分了解,对相同的纳米级材料特性的自动“交叉参照”远非一种自动化假设;它们在本质上是全新的材料。 人们逐渐意识到了对于这类材料的更长期潜在毒性作用及其潜在环境影响目前还知之甚少。 因此,人们对工程纳米材料的潜在毒性作用产生了兴趣并开展了大量的研究工作,同时也对现有产品及配方中纳米级成分的重要性作出评论。
在开始对悬浮纳米颗粒进行任何纳米毒理学研究之前,必须知道所用纳米颗粒的状态,尤其是其在相应试验介质中的粒度、粒度分布以及浓度。
粒度决定了扩散速度、对生物屏障或由其所引起的渗透率或排斥率以及颗粒相互作用。
本指南详述了如何使用纳米颗粒跟踪分析(NTA)技术表征生物学相关流体中的纳米金颗粒及其聚集体。 作为对经典的光散射技术的补充,NTA可以逐个地对悬浮液中的纳米颗粒测定粒度和浓度,从而更精准的了解聚集过程。 该研究着眼于纳米金颗粒粒度的变化,它将标准分散溶剂(柠檬酸盐缓冲液)的情况与稀释血浆(含蛋白质)进行对比(NIST [2007])。 [2007])。
血液采集自健康的献血者。 以800 RCF的离心力对试管进行离心操作5分钟,从而使红细胞和白细胞聚集。 将上清液(血浆)转移至贴有标签的试管中,并在零下80˚C的温度下保存。 解冻后,再以16.1 kRCF的离心力对血浆离心3分钟,以进一步减少红细胞和白细胞。 将上清液转移至一个新容器中,注意不要搅动颗粒。
采用直径为60 nm的NIST标准纳米金颗粒(NIST参考资料8013)。 它们按照NIST(2007)中的相关调查报告进行储存、制备和使用。 用pH值等于7.19的标准柠檬酸盐缓冲液,将纳米金颗粒稀释至大约108个颗粒/毫升的浓度。 对于血浆中的分散质,在柠檬酸盐缓冲液中将人血浆稀释1:106,并用790 µL的稀释血浆来稀释10 µL的纳米金颗粒。
在NanoSight LM10上进行纳米颗粒跟踪分析。 所有样品的制备和测定工作都是在爱尔兰的都柏林大学进行。 录制并批量分析了多段视频(每段时长166秒),以确保统计稳健性。 值得注意的是,鉴于血浆是一种天然离子介质,蛋白质聚集是一个永远存在问题。
分别稀释在柠檬酸盐缓冲液和人血浆中时,录制了纳米颗粒的视频(图1),同时跟踪和分析了粒度和浓度(图2)。
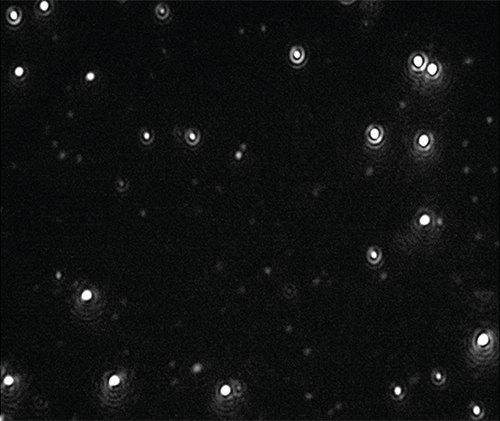
|
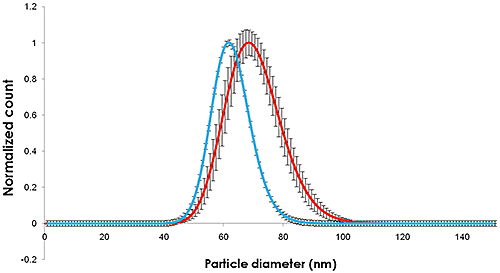
|
稀释于柠檬酸盐缓冲液中的金颗粒测定方法详见NIST(2007)的参考资料报告。
通过目视检查和浓度测定,NTA技术可用来确定颗粒仍具有单分散性,这就为悬浮液中的蛋白质发生反应而涂覆在纳米颗粒上(粒度变大与聚集现象无关)这一假设提供了新的证据。
图1和图2中所记录的粒度变化表明纳米颗粒的粒度增幅约为10 nm,这对应于覆盖纳米颗粒的5 nm厚的蛋白质吸附层。
在诸如人血浆这类生物介质中,单分散性纳米金颗粒的粒度变化是显著而可测的。 我们在这里介绍了一种利用纳米跟踪分析技术进行血浆层厚度测定的适用方法。
通过NTA测出的柠檬酸盐分散颗粒的粒度分布广度和平均值与NIST测定值相似。 在血浆中,粒度和粒度分布均出现类似增长。
NTA能够测定绝对浓度,利用该绝对浓度还可以得出NIST纳米金颗粒的计数浓度。 NTA也非常适合鉴别纳米颗粒聚集物并测定其浓度,例如,那些很容易区分的二聚体。 因此,它(对于这里使用的纳米颗粒和浓度测定法)在现有适用于工程纳米材料的生物纳米科学和生物纳米相互作用领域的一组技术中,是一种有用的工具。
人们认为NTA是一种可提供纳米颗粒粒度和同样重要的浓度信息的分析方法,即使在具有高度多分散性的复杂样品类型中也能够做到这一点。(Montes-Burgos等人,2010年;Lynch,2008年;Montes-Burgos等人,2007年)。 像NTA这样的方法被认为是未来可用于研究纳米颗粒的环境影响和潜在细胞毒性的众多方法之一(Borm等人,2006年;Tenuta,2008年;Tran和Anton,2009年;Kuhlbusch等人,2010年;Hassellöv和Kaegi,2009年;Stolpe等人,2011年)。
最近的研究表明,NP和环境基质间的相互作用是极其复杂的,对其量化和建模都是一个巨大的挑战;但是,NTA却能在其中提供一种进行研究与分析的机制(Gornati等人,2009年;Hartmann,2011年;Arvidsson等人,2011年;Howard,2010年;Njuguna等人,2011年;Tran等人,2009年)。
在零价纳米铁(nZVI)涂层对三种主要的海洋无脊椎动物早期生命发育阶段的影响这一研究中,Kadar等人 (2012年)利用 NTA技术研究了nZVI在海水中的溶解情况,表明涂层有助于稳定纳米金属悬浮液。 Kadar还研究了NTA分析的工业相关型工程铁纳米颗粒对海洋微藻培养基的生长和代谢状态的影响,其中他描述了其生长率、粒度分布、脂质特征及细胞超微结构随之而出现的改变(Kadar等人,2012年)。
对于大型蚤、淡水甲壳类和常见的毒性指标物种,使用15k寡核苷酸微阵列芯片来区分颗粒特异性毒性与银离子毒性,并为涂覆柠檬酸盐和聚乙烯吡咯烷酮的银纳米颗粒制作了暴露生物标记,Poynton等人 (2012年)在基因组水平下研究其毒性之前,先通过NTA确定了银纳米颗粒的聚集度。
在研究氧化锌纳米颗粒对Folsomia念珠菌的毒性时,Waalewijn-Kool等人 (2012年)表示,通过添加暴露介质而测试分散质粒度特性的方法与该生物体的生殖能力没有多大差别,NTA和TEM(电子显微镜)均表明氧化锌的毒性与粒度无关。
经证实,NTA在细胞水平下有助于研究钴纳米颗粒在人外周血白细胞(Colognato等人,2008年)和小鼠成纤维细胞(Ponti等人,2009年)中的基因毒性。 纳米颗粒穿过人胎盘的能力(Wick等人,2009年)和 研究这对其他生物屏障的影响的方法现已明确(Linn等人,2010年),其中包括运送二氧化硅纳米颗粒通过人体皮肤(Staroňová等人,2012年)。 同样地,Filon等人(2012年)报告了纳米钴颗粒穿过完好皮肤和受损皮肤时得出的人体皮肤渗透情况,表明作为纳米颗粒涂层的钴在体外扩散系统中能够渗入人体皮肤。
在其介入细胞系统进行细胞毒理学测试前了解纳米颗粒的粒度分布是非常重要的,NTA在这方面已被证实非常有用(Kendall等人,2009年;Patel等人,2010年;Munaro,2010年;Karlsson,2010年)。 其他的研究还包括不同类型的纳米颗粒与各种不同生物源性基质,例如血清(Treuel等人,2010年)、有机污染物(Ben-Moshe等人,2009年)以及二硫苏糖醇(Sauvain等人,2008年)之间的化学相互作用。
对于纳米钴颗粒(Co-NP)聚集体的毒性作用进行了检验,并使用代表肺、肝、肾、肠和免疫系统的不同细胞系,将其与钴离子的毒性进行了对比。 总体研究结果与“聚集性钴纳米颗粒的毒性作用主要归因于聚集性钴纳米颗粒分解出的钴离子”这一假设相符。 (Limor等人,2011年)。
Arvidsson R, Molander S, Sanden BA and Hassellov M (2011) Challenges in Exposure Modeling of Nanoparticles in Aquatic Environments, Human and Ecological Risk Assessment: An International Journal, Volume 17, Issue 1, 2011, Pages 245 - 262, DOI: 10.1080/10807039.2011.538639
Ben-Moshe T, Dror I and Berkowitz B (2009) Oxidation of organic pollutants in aqueous solutions by nanosized copper oxide catalysts, Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, Volume 85, Issues 3-4, Pages 207-211
Borm P, Klaessig FC, Landry TD, Moudgil B, Pauluhn J, Thomas K, Trottier R and Wood S (2006) Research Strategies for Safety Evaluation of Nanomaterials, Part V: Role of Dissolution in Biological Fate and Effects of Nanoscale Particles, Toxicological Sciences, 90 (1): 23-32
Colognato R, Bonelli A, Ponti J, Farina M, Bergamaschi E, Sabbioni E and Migliore L(2008) Comparative genotoxicity of cobalt nanoparticles and ions on human peripheral leukocytes in vitro, Mutagenesis Advance Access, published online 2008-5-25 and Mutagenesis 2008 23(5):377-382
Filon FL, Crosera M, Timeus E, Adami G, Bovenzi M, Ponti J, Maina G (2012) Human Skin Penetration of Cobalt Nanoparticles Through Intact and Damaged Skin, Toxicology in vitro, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2012.09.007,
Gornati R, Papis E, Di Gioacchino M, Sabbioni E, Dalle-Donne I, Milzani A and Bernardini G (2009) In vivo and in vitro Models for Nanotoxicology Testing, in Nanotoxicity (eds S. C. Sahu and D. A. Casciano), John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK. DOI: 10.1002/9780470747803.ch15
Hartmann NB (2011) Ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to freshwater organisms, PhD Thesis April 2011, Department of Environmental Engineering, Technical University of Denmark
Hassellöv M and Kaegi R (2009) Analysis and characterization of Manufactured Nanoparticles in Aquatic Environments. In: "Nanoscience and Nanotechnology: Environmental and human health implications." (Eds. Lead J.R. and Smith E.) Wiley Interscience, Chapter 6, p 211-266.
Howard AG (2010) On the challenge of quantifying man-made nanoparticles in the aquatic environment, J. Environmental Monitoring, 12, 135 - 142. DOI: 10.1039/b913681a
Kadar E, Rooks P, Lakey C, Whitea DA (2012) The effect of engineered iron nanoparticles on growth and metabolic status of marine microalgae cultures, Science of The Total Environment, Volume 439, 15 November 2012, Pages 8-17
Karlsson HL (2010) The comet assay in nanotoxicology research, Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry DOI: 10.1007/s00216-010-3977-0
Kendall M, Ding P, Kendall K and Clark H (2009) Nanotoxicology of PM: Particle interactions with lung surfactant polymers, IEH (2009) Proceedings of the Annual UK Review Meeting on Outdoor and Indoor Air Pollution Research, 20-21 April 2009 (Web Report W26), Institute of Environment and Health, Cranfield University, UK, available at: http://www.cranfield.ac.uk/health/ieh
Kuhlbusch TAJ, Fissan H and Asbach C (2010) Measurement and Detection of Nanoparticles within the Environment. Nanotechnology. p229-266
Limor H-A, James KC., Rafi K, Patrice NM, Oded M, Ponti J, Romano R, Rossi F, Golla-Schindler U, Sommer D, Uboldi C, Unger R and Villiers C (2011) Predictive toxicology of cobalt nanoparticles and ions: comparative in vitro study of different cellular models using methods of knowledge discovery from data, Toxicol. Sci. (2011) DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr124 First published online: 2011-5-20
Linn M, Loretz B, Philippi C, Vajda V (2010) Optical characterization of nanoparticles, 8th International Conference and Workshop on Biological Barriers - in vitro Tools, Nanotoxicology, and Nanomedicine, 21 March - 1 April 2010, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany
Lynch I (2008), NanoInteract - dispersion,cell culture standards, protocols, NanoImpactNet WP1 Workshop, UCD, Ireland, 20th June 2008.
Montes-Burgos I, Salvati A, Lynch I, Dawson K (2007), Characterization techniques for nanoparticle dispersion, at European Science Foundation (ESF) Research Conference on Probing Interactions between Nanoparticles/Biomaterials and Biological Systems, Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain, 3 - 8 November 2007
Montes-Burgos I, Walczyk D, Hole P, Smith J, Lynch I and Dawson K (2010) Characterization of Nanoparticle Size and State Prior to Nanotoxicological Studies, Journal of Nanoparticle Research, Volume 12, Number 1 / January, 2010 DOI: 10.1007/s11051-009-9774-z
Munaro B (2010) Mechanistic in vitro tests for genotoxicity and carcinogenicity of heavy metals and their nanoparticles, Dissertation zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades des Doktors der Naturwissenschaften Eingereicht im Fachbereich Biologie an der Universität Konstanz vorgelegt von June 2009 Konstanzer Online-Publikations-System (KOPS) URN: http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:bsz:352-opus-121714
National Institute of Standards & Technology, Report of Investigation, Reference Material 8013, Gold Nanoparticles, Nominal 60 nm Diameter 13/12/2007.
Njuguna J, Sachse S, Silva F, Irfan A, Michałowski S, Pielichowski K, Kazmina O, Ermini V, Zhu H and Blázquez M (2011) Investigations into nanoparticles generated from nanofiller reinforced polymer nanocomposites during structural testing, Safety issues of nanomaterials along their life cycle, Symposium at LEITAT Technological Center, Barcelona (Spain). 4th and 5th May 2011
Patel D, Kell A, Simard B, Xiang B, Lin HY and Tian G (2010) The cell labeling efficacy, cytotoxicity and relaxivity of copper-activated MRI/PET imaging contrast agents, Biomaterials, DOI:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.013
Ponti J, Sabbioni E, Munaro B, Broggi F, Marmorato P, Franchini F, Colognato R and Rossi F (2009) Genotoxicity and morphological transformation induced by cobalt nanoparticles and cobalt chloride: an in vitro study in Balb/3T3 mouse fibroblasts, Mutagenesis, Jul 2009; DOI:10.1093/mutage/gep027
Poynton HC, Lazorchak JM, Impellitteri CA, Blalock BJ, Rogers K, Allen J, Loguinov AV, Heckman L and Govindasmawy S (2012) Toxicogenomic Responses of Nanotoxicity in Daphnia magna Exposed to Silver Nitrate and Coated Silver Nanoparticles, Environ. Sci. Technol., DOI: 10.1021/es3001618
Sauvain J, Deslarzes S and Riediker M (2008) Nanoparticle reactivity toward dithiothreitol, Nanotoxicology, 2:3, 121 - 129
Staroňová K, Nielsen JB, Roursgaard MJ, Knudsen LE (2012) Transport of SiO2 Nanoparticles through Human Skin, Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2012.00873.x
Stolpe B, Lead J, Cole P, Kendall M, Kadar E, Poole J, Whitby C, Colbeck I, Fabrega J and Galloway T (2011) Multimethod characterization of manufactured nanoparticles in toxicity studies, 6th International Conference on the Environmental Effects of Nanoparticles and Nanomaterials, N1.7,The Royal Society, London, 19th-21st September, 2011.
Tenuta T (2008) A Systematic Approach to Assessing Potential Environmental Impacts of Nanomaterials: Nanoparticle Synthesis, Characterization and Impact Assessment, , EPA Scholarship & Fellowship Seminar - 13th November 2008, Hilton Kilmainham Hotel, Dublin 8, Ireland
Tran L and Antón JMN (2009) Nanotoxicology And Engineered Nanoparticle Risk Assessment, Seguridad y Medio Ambiente - Nº 114, p1 de 45
Treuel L, Malissek M, Gebauer JS and Zellner R (2010) The Influence of Surface Composition of Nanoparticles on their Interactions with Serum Albumin, Chem Phys Chem, Volume 11, Issue 14, pages 3093-3099
Waalewijn-Kool PL, Ortiz MD and van Gestel CAM (2012) Effect of different spiking procedures on the distribution and toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles in soil, Ecotoxicology. DOI: 10.1007/s10646-012-0914-3Online First™Open Access
Wick P, Malek A, Manser P, Meili D, Maeder-Althaus X, Diener L, Diener P-A, Zisch A, Krug H F. and von Mandach U (2009) Barrier Capacity of Human Placenta for Nanosized Materials, Environmental Health Perspectives DOI: 10.1289/ehp.0901200, (available at http://dx.doi.org/) Online 12 November 2009